Do you know the correct way to handle and disinfect your masks and respirators, which have now become a crucial daily necessity for us to wear, in order to ensure they serve their intended purpose effectively?

Unnecessary Disinfection of Disposable Masks Due to Improper Use
Surgical masks or non-nanofiber mouthpieces are designed for single-use protection only. Disinfecting them is futile, and once used, they should be disposed of immediately.
Why Isn´t Possible to Disinfect Them, and What Is the Reasoning behind It?
Disposable masks operate on the principle of electrostatic charge, utilizing a non-woven fabric that is electrostatically charged and folded into three layers. This charge attracts smaller particles and droplets, effectively protecting the wearer and those around them. However, both disposable and cloth masks lose effectiveness when they become wet, which is why they should not be disinfected. Once wet, the electrostatic charge dissipates, rendering the mask ineffective after a short period of use (often stated as around 120 minutes). Any attempt to disinfect the mask will also damage the electrostatic charge and render it ineffective, as disinfectant solutions and water will compromise the material.
Nanofiber Masks - Can Be Repeatedly Disinfected (if Necessary)
Nano masks differ from regular surgical masks in their material composition, as they contain a highly effective layer of nano-fiber membrane in addition to non-woven fabrics. This layer is approximately 100 times denser than the non-woven fabric layers, and can capture up to 99.9% of bacteria and viruses due to its unique material composition.
#produkty#https://www.nanospace.store/nano-face-masks/
According to standard classification, nanofiber masks are disposable materials, but they can be disinfected 1-3 times if required. Unlike disposable masks that operate on the principle of electrostatic charging, nanofiber masks capture viruses through a nanofibrous membrane that only loses effectiveness due to mechanical damage or clogging.
Tip: Instead of disposable masks, try a designer washable mask.
How to Disinfect a Nano Mask
By spraying with a suitable ethanol disinfectant - the mask must not get wet and you must then let it dry completely.
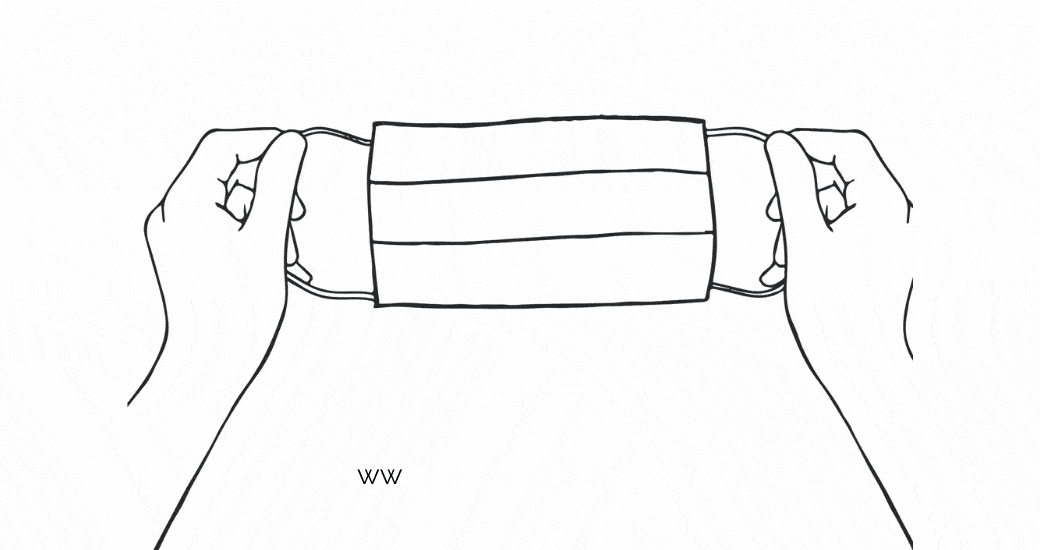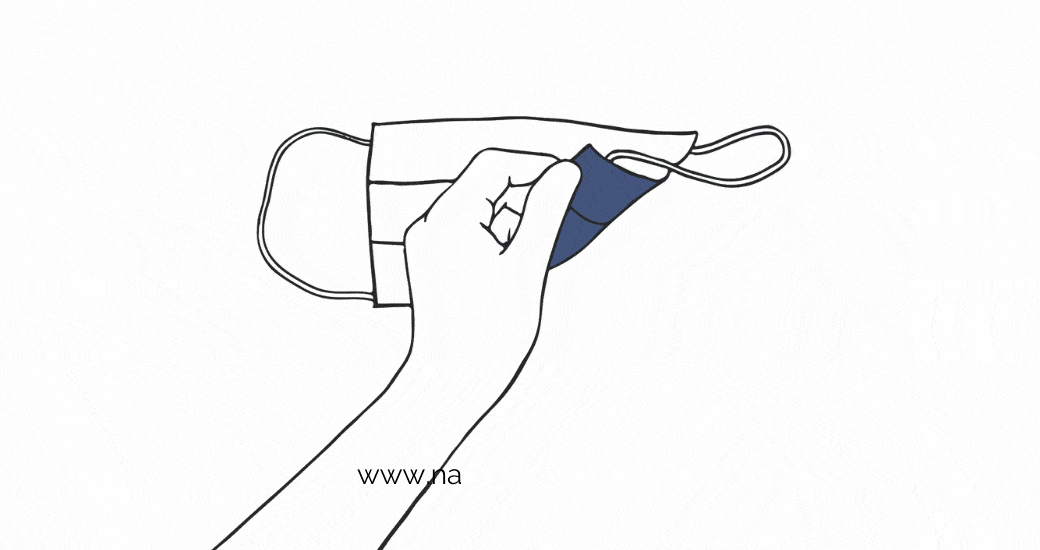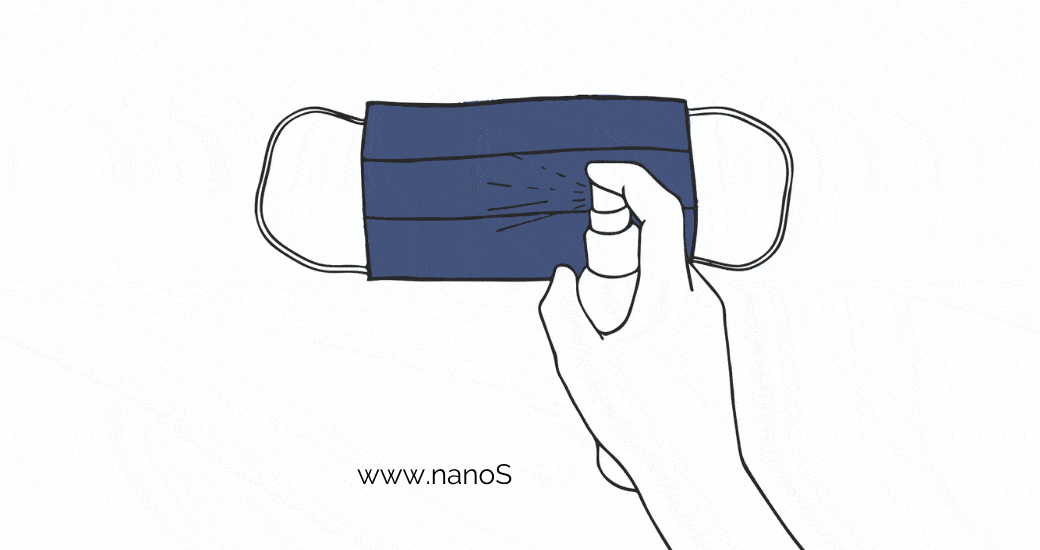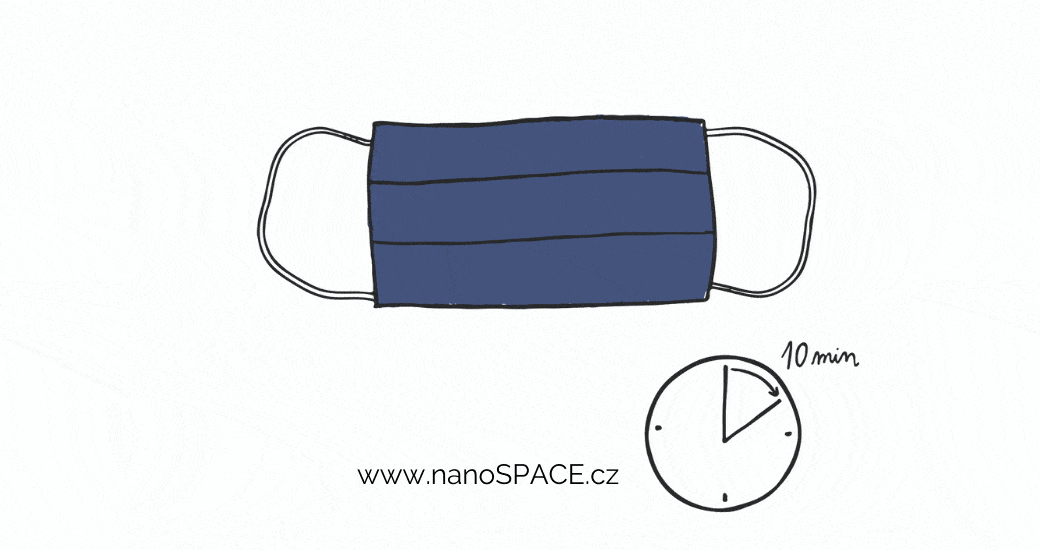
The disinfection process for nano masks may vary depending on the manufacturer. Ethanol disinfection is a common method, although other methods may also be recommended. Always check the recommended disinfection method for your specific nano mask before sterilizing. It's important to note that washing, boiling, ironing, or microwaving nano masks is not recommended.
Tip: When traveling, we recommend travel disinfectant spray in your pocket.
Four Effective Methods for Sterilizing Masks:
- using a sterilization autoclave – at max. 85 °C for 20 minutes
- in a hot air oven for 20 minutes at 75 degrees
- using a germicidal (UV-C) lamp for 15 minutes
- using an ozone sterilizer for 15 minutes
Textile Masks - Disinfection Is a Must
Disinfecting cotton textile masks, whether homemade or purchased, is essential for their repeated use. To improve their effectiveness against bacteria and viruses, nano filters can be inserted into these masks. However, before disinfecting the cloth mask, it's important to remove the filter and disinfect it separately using one of the methods mentioned earlier or replace it with a new one.
#produkty#https://www.nanospace.store/search/?string=disinfection+of+masks+and+respirators
How to Disinfect a Textile Mask
- Machine wash them at a minimum temperature of 60°C for at least 30 minutes. There's no need to iron the masks after washing.
-
Boil the masks in a pot on the stove for at least 5 minutes. After boiling, let the masks cool in water. Ironing is not necessary.
Tip: When washing by hand or in a washing machine, use a gentle washing gel on cotton masks scarves and masks BAMBOO Gold.
Simply ironing textile masks is not sufficient to eliminate all microorganisms. Disinfecting masks in a microwave oven is also not recommended due to the risk of ignition. Freezing masks is also ineffective since viruses are resistant to frost and there is a risk of food contamination.

