Do you have oily skin and suffer from pimples that can't be squeezed? Then it's likely subcutaneous acne. This manifests as inflamed pimples that appear beneath the skin's surface and are often very painful. Let's take a look at what causes subcutaneous acne and what helps with blind pimples.

What is Subcutaneous Acne
Subcutaneous acne is a type of acne, also known as cystic acne or dermatosis, where pimples form much deeper beneath the skin's surface and are often inflamed. They can be very painful and can even leave scars on the skin. It occurs when sebaceous glands become clogged, leading to the accumulation of sebum under the skin along with bacteria and dead skin cells, which then cause inflammation.
What Subcutaneous Acne Looks Like
Every problematic skin suffering from acne may appear similar at first glance, yet they differ from each other. Subcutaneous acne can appear as inflammatory or non-inflammatory pimples that are deep beneath the skin's surface, causing them to be painful and making treatment difficult.
Tip: Try the effective NAFIGATE acne cream.
Subcutaneous acne can appear as a reddened and swollen area with larger pimples that are painful to touch. Swelling results from the accumulation of pus and bacteria deep beneath the skin's surface.
How Subcutaneous Acne Forms
Just like with classic acne, subcutaneous acne arises due to excessive sebum production, which accumulates deep beneath the skin's surface along with dead cells. Sebaceous glands not only get clogged, but inflammation occurs, leading to painful cysts and pus formation.
How Subcutaneous Acne Manifests
Suffering from acne and not sure if it's subcutaneous acne or something else? Several types of acne can appear on the skin simultaneously. Subcutaneous acne can manifest in several ways.
- Pustules: They have yellowish or white heads and are among the most common types of subcutaneous acne.
- Papules: These are small red pimples inflamed due to the presence of bacteria.
- Cysts: These large, deeply rooted swellings are full of pus and can be very painful and soft to the touch. They often burst, usually leading to infection.
- Nodules: Smaller nodules, which can also be hard, reddened bumps located deep beneath the skin's surface and can be sensitive to touch. If they are hard, it means they have been under the skin for several weeks or months.
Subcutaneous acne most commonly manifests on the face, chin, neck area, but also on the back and chest.
#produkty#https://www.nanospace.store/skin-cleansing:nafigate/?order=name
TIP: 10 effective tips to get rid of acne.
What Causes Subcutaneous Acne
Now that you know how subcutaneous acne forms, let's look at what can influence sebum production:
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal imbalance often associated with puberty, pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause can increase sebum production and thus the risk of subcutaneous acne.
- Use of contraceptives or medications: Certain forms of contraception and medications, such as corticosteroids, anabolic steroids, or drugs containing halogens – chlorine, fluorine, and bromine, can affect hormone levels and thus the risk of acne.
- Bacteria: The presence of excessive bacteria on the skin can cause infection of the sebaceous glands and hair follicles, leading to inflammation and the formation of subcutaneous acne. Bacteria most commonly reach the skin through frequent touching.
- Quality of skin care: Inadequate skin cleansing, use of unsuitable cosmetic products, or aggressive treatments can worsen the problem of subcutaneous acne.
- Lack of balanced diet: Lack of foods containing vitamins and minerals, especially omega-3 fatty acids, can affect skin health and increase the risk of subcutaneous acne.
What Helps with Subcutaneous Acne
Subcutaneous acne is painful and unpleasant. If it's in a severe condition, individual treatment recommended by a dermatologist is usually necessary. They typically suggest products with retinoids. If subcutaneous acne isn't severe, you can manage it at home. What helps with pimples that can't be squeezed?

Tip: How to Properly Cleanse Your Skin?
Skincare
Whether you have dry skin or oily skin with subcutaneous acne, proper skincare is essential. The foundation is thorough cleansing with a gentle face wash for sensitive skin that soothes irritation and redness. At the same time, it's necessary to hydrate and nourish the skin and, most importantly, apply effective ingredients that combat acne in the form of creams, masks, or topical acne treatments.
Acne Cosmetics
When choosing acne products, it is important to consider two main active ingredients: salicylic acid, which helps to cleanse pores and accelerate skin exfoliation. And benzoyl peroxide, an effective substance that kills bacteria on the skin and thus helps treat acne.
- Acne Cream: Even problematic skin needs hydration and nourishment. For this purpose, acne creams are designed, which also have anti-inflammatory effects.
- Acne Masks: For more extensive acne, it's suitable to treat the skin with an effective acne mask that absorbs impurities, regulates sebum production, and soothes the skin.
- Acne Patches: For local application, nano-fiber acne patches work excellently, delivering active ingredients directly to problematic areas.
Tip: How Do Acne Patches Work?
Retinoids and Subcutaneous Acne
Retinoids are derivatives of vitamin A and are often prescribed for problematic skin with acne, but they are suitable for all skin types. They help renew cells, regulate sebum production, reduce inflammation, and help unclog pores by removing dead skin cells. When choosing products with retinoids, it's important to select those with lower concentrations to avoid irritation of sensitive skin.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peeling using alpha-hydroxy acids or beta-hydroxy acids can be an effective way to get rid of subcutaneous acne. These acids work to remove dead cells to prevent inflammation and the formation of new pimples. This process is called exfoliation. By removing dead cells, pore and sebaceous gland blockage is reduced, making it a great way to prevent acne.
#produkty#https://www.nanospace.store/cosmetics:nafigate/?pv274=2428
Tip: NAFIGATE Acne Mask can absorb impurities from skin pores and regulate sebum production with natural polymer P3HB.
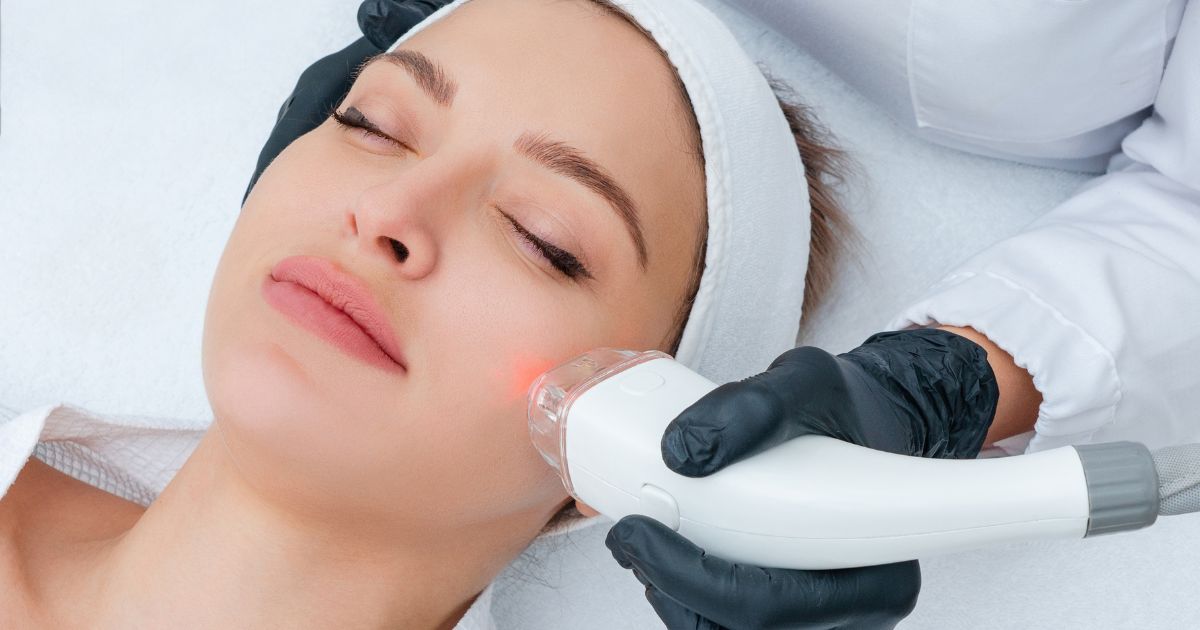
Subcutaneous Acne Laser Treatment
Laser treatment can suppress sebum production and be helpful in inflammation. This prevents the spread of inflammation and gradually makes it disappear. And by limiting sebaceous gland production, new subcutaneous acne is less likely to form.
TIP: Try Acne Cream NAFIGATE with salicylic acid.
Avoid Squeezing Pimples
Subcutaneous acne is a form of acne characterized by pimples forming deep beneath the skin's surface. That's why pimples can't be squeezed. So when you attempt it, the problem with subcutaneous acne is likely to worsen. Why shouldn't you squeeze subcutaneous acne?
- Hair Follicle Depth: Subcutaneous acne forms deep beneath the skin's surface, meaning the pimple is deep below the surface. Attempting to squeeze it can lead to damaging surrounding tissues and causing inflammation to spread.
- Infection Risk: By introducing dirt and bacteria from unwashed hands into the pimple, there's a risk of infection. This can lead to even more severe inflammation and worsen the overall acne condition.
- Permanent Scarring: Attempts to squeeze deep pimples can leave permanent scars visible on the skin even after the acne has healed.
- Pain: Subcutaneous acne is often painful on its own. Attempting to squeeze it can cause even more pain.
Tip: Small scars can be helped by rejuvenating nanofiber masks from nanoBeauty.
Change in Dietary Habits
What you eat reflects on overall health and skin health. You can alleviate subcutaneous acne by avoiding sugar and starch in foods, which can increase insulin levels and the risk of nodules and cysts. Include more fruits and vegetables in your diet to ensure you get enough vitamins and minerals.
Tip: Give your skin the best and nourish it internally with 5-in-1 collagen for beautiful skin – Collagen peptides plus..
How to Remove Acne Scars
Subcutaneous acne often leaves smaller or larger scars, dark or purple spots at the site of injury. While scar formation and 100% healing cannot be prevented, it can be somewhat reduced.
Scars are most commonly caused by squeezing pimples. Chemical peeling can effectively remove old skin cells, which are than gradually replaced by new ones. Thanks to this peeling, skin brightens, smoothes, and renews, reducing not only smaller scars but also minor wrinkles.
Tip: What are the benefits of acids in cosmetics?
Purple Discoloration After Acne
After healing subcutaneous acne on the skin, red or purple spots often remain. These are evidence that the body fought acne. This discoloration may be visible for several months, and you can get rid of it with proper skincare or laser treatment.
TIP: For even skin tone and nourishment, try brightening nanofiber masks for acne from nanoBeauty.
Home Remedies for Subcutaneous Acne
Want to get rid of subcutaneous acne with natural products? It's possible, but expect this path to be longer and far less effective than specialized acne products. Natural methods for removing subcutaneous acne are more suitable as overall health support, supplementing vitamins and minerals, or adjusting diet for healthy skin.
- Green Tea: Green tea is rich in antioxidants, which can help reduce inflammation and fight against inflammatory subcutaneous acne. You can prepare a cup of green tea and use it as a compress on the affected area or make a toner by mixing it with cold water and applying it to the skin with a cotton pad.
- Natural Probiotics: Probiotics help maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in the intestines and can therefore help prevent subcutaneous acne. Natural probiotics include yogurts, kefirs, pickled vegetables, or fermented beverages such as kombucha.
- Aloe Vera: Aloe vera has soothing and anti-inflammatory effects that can help alleviate subcutaneous acne and can also be found in many cosmetic products. You can apply aloe vera gel to the affected area to soothe it.
#produkty#https://www.nanospace.store/cosmetics:nanobeauty,nfibrecare/?pv274=2428
Tip: Aloe vera: What Are Its Effects on Skin and Complexion?
Prevention and How to Avoid Subcutaneous Acne
Although subcutaneous acne can result from hormonal changes or genetics, which we cannot influence much, there are several tips to at least partially prevent subcutaneous acne.
- Regular skincare,
- quality acne products,
- adequate exercise because sweat cleanses pores,
- limitation of alcohol and smoking,
- healthy diet,
- avoiding stress,
- quality sleep,
- not touching the skin during the day,
- proper hydration.
Tip: Are you stressed for a long time? Try dietary supplements to induce positive mood and relaxation with vitamins.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How to Squeeze Subcutaneous Acne
Subcutaneous acne cannot be squeezed, so do not attempt it. Instead, use acne masks or local acne patches.
How to Pierce Subcutaneous Acne
Piercing subcutaneous acne should be done by a professional, such as a dermatologist. Do not take it into your own hands as you may cause infection or scarring. The doctor can use a sterile needle to pierce the cyst and then clean the area.
What Helps with Subcutaneous Acne on the Back
When trying to treat subcutaneous acne on the back, regular personal hygiene is important, especially after exercising and excessive sweating. Also helpful is clothing made of breathable materials that won't irritate the already irritated skin. And last but not least, the use of acne products.
How to Quickly Get Rid of Subcutaneous Acne?
Since subcutaneous acne is one of the most severe forms of acne, treatment is usually long. For quick healing of localized subcutaneous acne, you can try acne patches, acne masks, or consult a dermatologist.
Sources
- Ahramiyanpour, N., Rastaghi, F., Parvar, S.Y., Sisakht, A.K., Hosseini, S.A. and Amani, M., 2023. Subcision in acne scarring: a review of clinical trials. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 22(3), pp.744-751.
- Balighi, K., Robati, R.M., Moslehi, H. and Robati, A.M., 2008. Subcision in acne scar with and without subdermal implant: a clinical trial. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 22(6), pp.707-711.
- Arif, T., 2015. Salicylic acid as a peeling agent: a comprehensive review. Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology, pp.455-461.
- Pullar, J.M., Carr, A.C., & Vissers, M.C.M. (2017). The Roles of Vitamin C in Skin Health. Nutrients, 9, 866.

